How Does a Vaulted Ceiling Work?
Vaulted ceilings, a prominent architectural feature dating back to ancient times, have captivated architects and homeowners alike for centuries. These ceilings, characterized by their arched or curved construction, not only enhance the aesthetics of a space but also contribute to its structural integrity and thermal efficiency. This article explores the workings of vaulted ceilings, delving into their design, construction, and benefits.
Structural Principles of Vaulted Ceilings
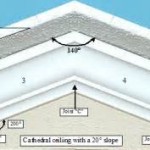
The essence of a vaulted ceiling lies in its ability to distribute weight and forces effectively. Unlike flat ceilings that rely solely on beams for support, vaulted ceilings leverage the inherent strength of arches. Imagine a series of bricks arranged in a curved shape. The bricks, when arranged in this manner, exert outward thrusts, which are counteracted by the adjacent bricks and by the walls or columns supporting the arch. This principle, known as "arch action," is the core of vaulted ceiling construction.
The shape of the arch, whether pointed, rounded, or segmental, influences its load-bearing capacity. Pointed arches, often seen in Gothic architecture, are known for their strength and ability to span larger distances. Rounded arches, with their gentler curvature, are better suited for shorter spans. Both types effectively distribute the weight of the roof and ceiling above, minimizing the need for numerous supporting columns or beams within the space.
Construction Techniques
The construction of vaulted ceilings involves specific techniques depending on the type of material used. Traditionally, vaulted ceilings were built using masonry materials like brick or stone. These materials are strong and durable, but the construction process is labor-intensive and requires skilled masons. Modern vaulted ceilings, on the other hand, often utilize lighter materials such as wood, steel, or concrete, which are easier to work with and offer greater flexibility in design.
Wood-framed vaulted ceilings typically employ trusses, which are prefabricated structures consisting of interconnected beams and panels. These trusses are assembled on-site and lift into place, forming the framework for the ceiling. Steel frames, often utilized for larger spans and heavier loads, offer similar advantages in terms of speed and efficiency. Concrete vaulted ceilings, while more durable, require specialized formwork and pouring processes.
Benefits of Vaulted Ceilings
Vaulted ceilings offer a multitude of benefits, ranging from aesthetics to functionality. Their arched design creates a sense of grandeur and spaciousness, enhancing the overall visual appeal of a room. The taller ceilings also improve the flow of air and light, providing a more open and inviting atmosphere.
Beyond aesthetics, vaulted ceilings contribute to the structural integrity of a building. By effectively distributing weight and forces, they reduce the need for internal supports, opening up floor space and creating a sense of openness. In addition, their arched shape can enhance the thermal performance of a building by providing insulation, particularly in areas with extreme climates.
Types of Vaulted Ceilings
Vaulted ceilings are not monolithic structures; they come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics. Some common types include:
- Barrel Vaults: These are the simplest form of vaulted ceilings, resembling a half-cylinder. They are often found in hallways, corridors, and other elongated spaces.
- Groin Vaults: Two barrel vaults intersecting at a right angle create a groin vault, a common feature in medieval architecture. This type of vault provides strength and stability, making it suitable for larger spaces.
- Rib Vaults: These vaults incorporate ribs or beams along the arch's edges and at its intersections. Rib vaults offer greater structural support and were widely used in Gothic cathedrals.
- Fan Vaults: These vaults are characterized by their fan-shaped ribs that converge at a central point. Fan vaults create a sense of dynamism and are often found in grand spaces like churches or palaces.
Understanding the design, construction, and benefits of vaulted ceilings sheds light on their enduring appeal in architecture. From their structural prowess to their aesthetic charm, these ceilings continue to captivate and inspire, adding a touch of grandeur and functionality to any space they adorn.
Five Cathedral Ceilings That Work Greenbuildingadvisor
House Tweaking
Supporting A Half Vaulted Ceiling Fine Homebuilding
Vaulted Ceilings 101 The Pros Cons And Details On Installation Bob Vila
How To Vent A Cathedral Hip Roof The Right Way Roofing Plumbing And Ventilation Supplies
Planning A Vaulted Ceiling Everything You Need To Know Checkatrade
The Ultimate Guide To Vaulted Ceilings Pros Cons And Inspiration
What Is Vaulted Ceiling 11 Diffe Types Of Advantages And Disadvantages Ceilings Cost
Five Cathedral Ceilings That Work Fine Homebuilding
How To Support A Cathedral Ceiling Or Vaulted Roof
Related Posts